Explain the Differences of Public Offerings Versus Private Placement
Initial Public Offering IPO vs. One the IPO is a very public manner in which your business can expand and involve outside investors while a private placement is less spectacular but can be equally effective in helping.

What Is A Private Placement A Quick Guide To A Big Investment Investing Initial Public Offering Finance Planner
Provide a recent example of corporations using each type of offering.

. When a company issues shares to a select group of investors instead of inviting public at large it is called private placement of shares. Private placement of shares or convertible securities by listed issuer can be of two types. More regulated when compared to a private placement.
A private placement is a fundraising method where the stocks are sold to pre-selected investors and institutions rather than on the open market. As the name suggests a private placement is a private alternative to issuing or selling a publicly offered security as a means for raising capital. A private debt offering is also known as a private placement.
Private companies that seek to raise capital through issuing securities have two options. Explain the difference between public debt offerings and private debt offerings. Public Offering is one of the methods of selling securities to the general public where.
Private Placement Melanie James 2020-12-08T185345-0800 Issuers have various ways they can raise capital. When a business needs more capital than it generates it has two choices. The following are the advantages of private placement.
Transactions are smoothers and a lot of crucial time is saved by not having to register through the Stock Exchange. Both private placements and public offerings such as initial public offerings are ways for you to. Whereas it becomes easier to raise capital from private placement within a few months.
The two primary options for accessing funding includes a public offering by an investor or a private placement at a financial institution. Any business can offer shares of stock or bonds to select investors as a private placement -- the. The number of shareholders remains the same.
As per Section 42 of the Companies Act 2013 private placement can be defined as an offer to subscribe the securities of the company to a selected group of persons with a motive for fundraising other than the public offering. 5 rows 1. In a rights issue the company does offer the right issue of shares through a public offering.
In a private placement the company does not offer their stocks through a public offering. In other words A Private Placement refers to the offer of placement financial securities such as stocks bonds or debentures to the selected. Private and public companies reach out to outside investors to raise capital by selling their securities.
The biggest advantage with respect to private placements is the fact that most regulations governing public offerings do not come into play. These are very competitive. Explain the Differences Between Private Placement Public Offering.
Differences Between Private Placement Public Offering Both private placements and public offerings such as initial public offerings are ways for you to raise money to grow your business. Difference between Private Placement and Preferential Allotment under Companies Act 2013 For a Layman Private placement or non-public offering is a funding mode through Shares or Other Securities which are sold not through a public offering but rather through a private offering mostly to a small number of chosen investors. Private placement of shares can be issued by both public and private companies whereas in the case of the public offering the company is either listed or will be listed after the offer is made.
14 rows The key difference between Direct Public Offerings and Private Placements is that DPOs can. Capital is financial assets or financial value that businesses use to generate profit for further expansion and investment. A company willing to raise capital through fresh issue by going for public issue of shares has to go through a lot of procedures that will be time consuming.
The Securities Act of 1933 allows for private placements also known as unregistered offerings through several safe harbor exemptions found in Regulation D. Less regulated when compared to a rights offering. It is a faster way of raising capital as a company has to comply with fewer requirements.
Private debt offerings do not have to be registered with the SEC. Take out a loan or sell a. It is held in private to a select group on investors.
Offering securities to the public or. Finally by comparing the determinants of discounts for the case of private placement to those for the case of public offerings we show that under reasonable allocation constraints for public offerings the value of information has a greater impact on the discount level in private offerings compared to public offerings. In Private Placement companies sell securities directly to a few numbers of investors or institutions 2 Usually large scale companies uses Public Issue to raise funds Generally small scale companies raises funds through Private Placement 3 For Public Offering floatation cost is included since there is a requirement of an underwriter.
A private placement is different from a public issue in which securities are made available for sale on the open market to any type of investor. Investors involved in private placements are usually large banks mutual funds insurance companies and pension funds. It falls neither in the category of a public issue nor a rights issue.
The securities are sold to a group of investors in the private placement of shares whereas in a public offering the securities are offered to the public. A private placement is a sale of securities to a pre-selected number of individuals and institutions. Since the bonds are not public the financial information is not required to be published and they do not require a credit rating.
Difference of Private Placement Stock VsIPO Raising Capital. In a private placement both the offering and sale of debt or equity securities is made between a business or issuer and a. Private placement is a way for companies to sell securities to investors without being subject to the typical SEC registration and filing requirements.
Private placements are relatively unregulated compared to sales of securities on the open market. An initial public offering IPO also known as a public offering relates to the process of allowing shares of a private corporation to trade for the public in a new stock issuance.
/GettyImages-1220909109-917114c3d73d484da4dba1b81c4a8c66.jpg)
Initial Public Offering Ipo Definition
/dotdash_Final_Private_Equity_Apr_2020-final-4b5ec0bb99da4396a4add9e7ff30ac03.jpg)
Private Equity Definition How Does It Work
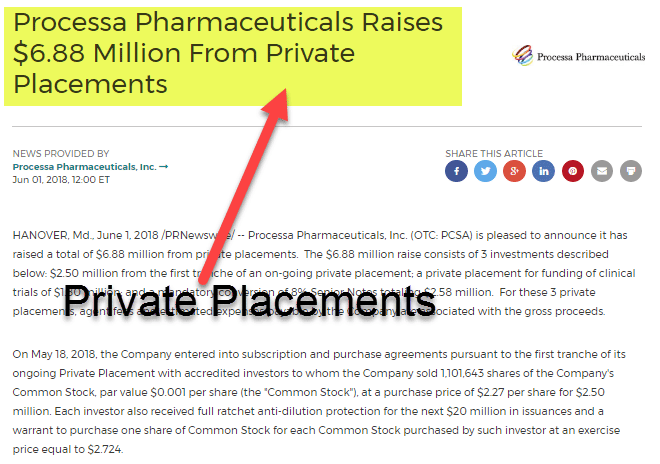
Private Placement Of Shares Top Advantages Disadvantages

Offering Memorandum Overview Example And Contents

Difference Between Private Placement And Preferential Allotment With Table Ask Any Difference

Ipo Process Select Investment Banker Documentation Pricing Etc Efm

Primary And Secondary Markets 2021 Bankingprep

Private Placement Memorandum Legal Forms Memorandum Memorandum Template

Pin On California Securities Law

Initial Public Offering Ipo Explained Westpac
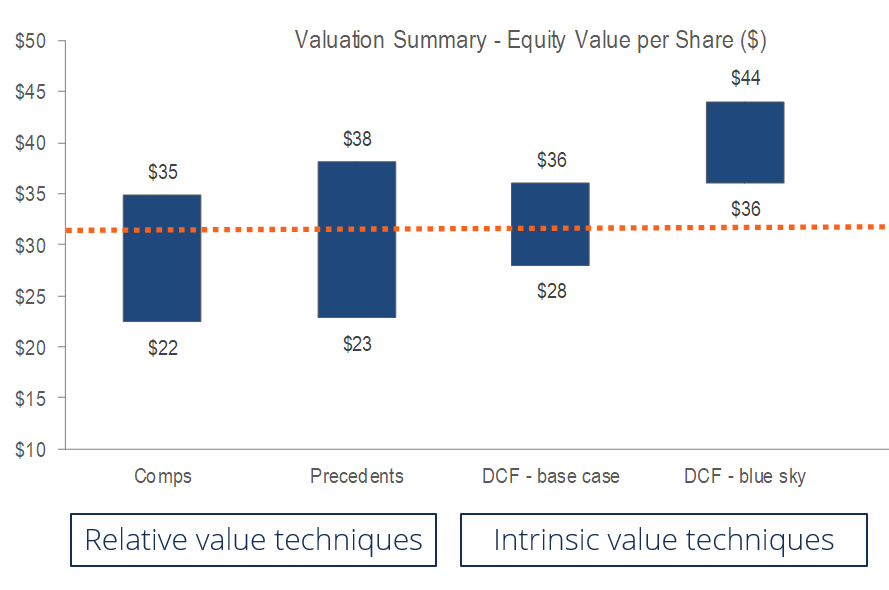
Ipo Initial Public Offering How Companies Are Valued And Listed
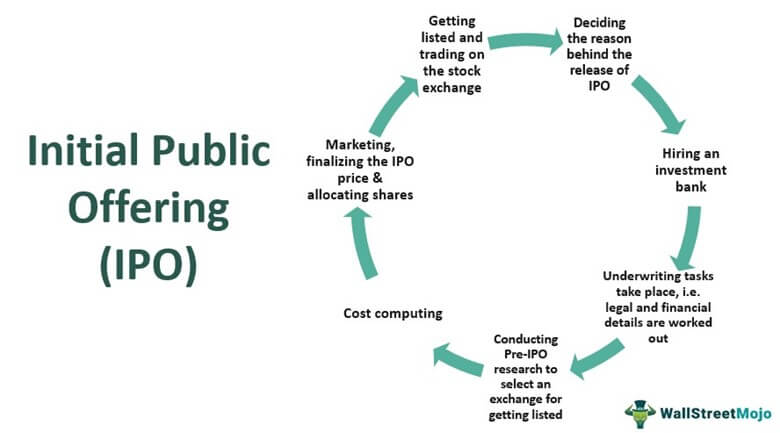
Initial Public Offering Ipo Definition Process How It Works
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Private_Equity_Apr_2020-final-4b5ec0bb99da4396a4add9e7ff30ac03.jpg)
Private Equity Definition How Does It Work

Initial Public Offering Ipo Definition Process How It Works

Difference Between Rights Issue And Private Placement

What Is The Meaning Of Primary Market What Is Marketing Raising Capital Meant To Be

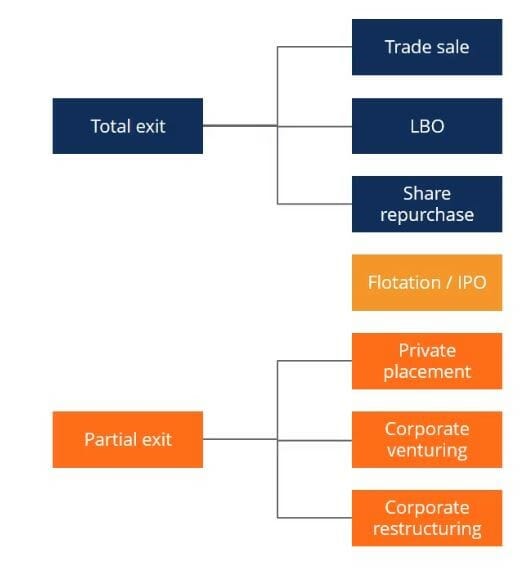
Comments
Post a Comment